Table of contents
- What is Java Script ?
- Basic intro and starting :
- How to link with HTML :
- Variable :
- Data Types :
- Operators :
- Comments :
- Print or Write :
- Functions :
- Loops :
- Arrays :
- Objects :
- If-Else :
- Switch-Case Statement :
- Template Strings :
- Jump Statements :
- Events :
- this Keyword :
- DOM :
- DOM Methods :
- BOM :
- BOM Methods :
- Closures :
- Modules :
- CallBacks() :
- Promises :
- Await :
- Strict Mode :
- Async :
- JS Projects for Begineer :
Hey folks ! Welcome again in my new blog & in this blog I'm gonna cover almost everything about JavaScript so, If you're having zero knowledge of Js then also you are most welcome. Here I'll try to cover every point that's necessary to know about JavaScript for fresher.
What is Java Script ?
So, JavaScript is a lightweight, cross-platform, and interpreted scripting language. It is well-known for the development of web pages, many non-browser environments also use it. JavaScript can be used for Client-side developments as well as Server-side developments
Basic intro and starting :
↪ Used to make web pages Interactive.
↪ File Extension: file_name.js
How to link with HTML :
🌟There are 2 ways to link a js file with an HTML file :-
- "External JS"
- "Internal JS" using the < script > tag
Variable :
🔴 Container used to store data (of different types).🌟 3 ways to create it
With var keyboard
var name = data-of-any-data-type;
With let Keyboard
let name = data-of-any-data-type;
With const keyword
const name = data-of-any-data-type;
Data Types :
🔴 " Type of a particular data is called data types "
🌟 There are 7 data-types in Js
String ➡ var a = "Hashnode";
Number ➡ var a = 5;
Boolean ➡ var a = True/False;
Array ➡ var a = [1, "a", true];
Object ➡ var a = {prop: "val"};
Null ➡ var a = null;
Undefined ➡ var a;
Operators :
🔴 " Symbols to perform operation on data "
🌟There are 4 operator types in JS
Arithmetic Operators (+,-,*,/,%)
Assignment Operators (=, +=,......)
Comparison Operators (>, <, ==, ......)
Logical Operators (&&, ||, !)
🚀 Example :-
var a = 10;
var b = 20;
var c = a+b;
Comments :
🔴 " Statements that are not executed while execution "
🌟There are 2 to write them in JS :
- Single Line Comment
//single line
Multi Line Comment
/ * multi line comment * /
Print or Write :
🔴 " Printing or Writing something on a screen. "
🌟There are 2 ways to print/write in JS :
- ☝🏼 On Browser Console
console.log("anything");
- ✌🏼 On document/screen
document.write("anything");
Functions :
🔴 " Block of code that perform a specific task "
🌟There are 2 to write them in JS :
🟩 Regular Function
let name = function( parameters )
{//code}
🟩 Arrow Function
let name = ( parameters ) =>
{//code}
Loops :
🔴 " Used for repeated execution of code until a certain condition "
🌟There are 3 types of Loops in JS :
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Do-While Loop
Example :-
# For Loop
for( init; condition; var++/--)
__________________________________
# While Loop
while ( condition ){ }
__________________________________
# Do-While Loop
do { code } while ( condition )
Arrays :
🔴 " Collection of data stored under the same name. "
🌟Data could be of any type
Syntax :
let arrayName = [ item0, item1,....... ];
note : Location of an item in an array is called Index of an Array
Array always starts from 0th Index
🌟 Multi-Dimensional Array :
↪ " Array within an array"
Objects :
🔴 " Collection of data store in form of name/value pairs. "
🌟Syntax :
let objectName = { name : "value" };
Here, name = property & value = Value
If-Else :
🔴 " Executes the code if the condition is true, else another code. "
🌟Syntax :
if ( condition == true ) {
// execute this code
} else {
// execute this code
}
Switch-Case Statement :
🔴 " It has 1 expression and some cases. Cases compare with expression. "
🌟Syntax :
switch ( expression ) {
case a :
// code
break;
case b:
// code
break;
default:
// code
}
Template Strings :
🔴 " New way to write strings using back-ticks ( ` ` ). "
🌟Syntax :
let str = `Hello`;
🌟Easy Interpolation :
( insertion of variables in the string ).
let name = "Hashnode";
let str = `Hello ${ name }` ;
// Output : Hello Hashnode
Jump Statements :
🔴 " Statements to transfer the control from one place to another. "
🌟return value ;
↪return value to the calling code.
🌟break ;
↪stops the execution.
🌟continue ;
↪control jumps to beginning of loop
Events :
🔴 " Action occurs when user interact with the web page. "🌟Example : Button clicked
🌟Syntax :
< element onevent = 'some Javascript'>
Here, "oneventname " eg. onclick
and "some Javascript" -> js code to be execute
this Keyword :
🔴 "
thisis a pre-defined words that always points to Js object. "
↪ Globally, it represents thewindow object.
↪In-object method, it represents theobject.
↪In function, it represents thewindow object.DOM :
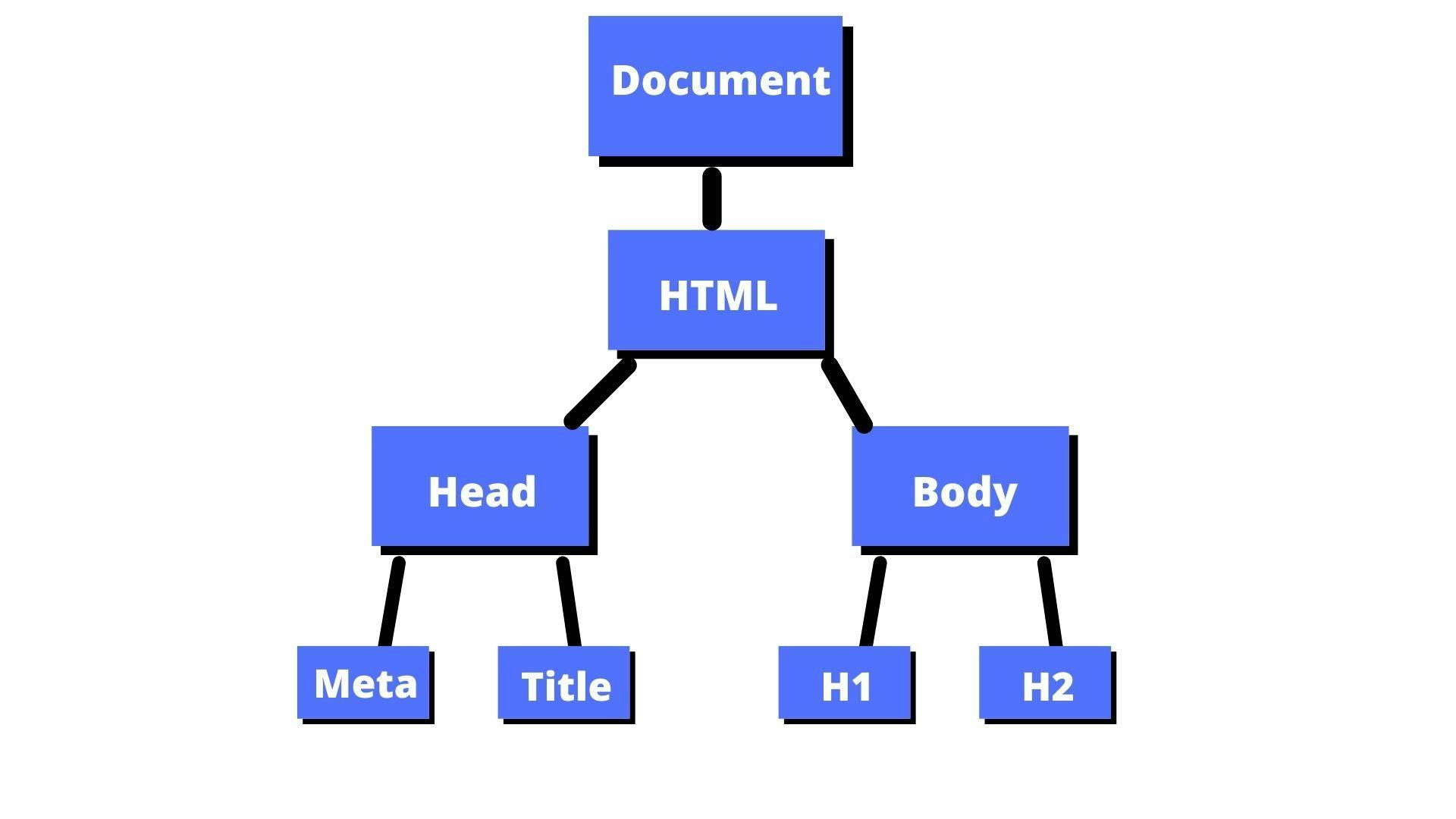
🔴"Document Object Model"
🌟 It looks like a Tree
🌟Tree of all HTML elements
🌟Everything (element, text, attribute) is called Node.
DOM Methods :
🔴 " These are the methods to access the DOM node or element. "
document.method();
🌟 .getElementByld
🌟.getElementsByTagName
🌟.querySelector
BOM :
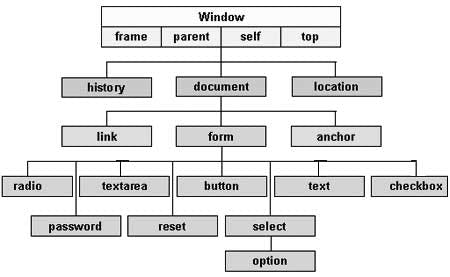
🔴"Browser Object Model"
🌟It also looks like a Tree
🌟Tree of all browser objects
🌟This include the info about the browser.
BOM Methods :
🔴 " These are the methods to access the BOM node or element. "
window.method()
🌟.open()
🌟.resizeTo()
🌟.close()
Closures :
🔴 " Feature in JS where inner function has access to outer function's variables. "
🚀 Example :
function hello(){
var a = 10;
var b = 20;
function print(){
var c = a+b;
console.log(c);
}
print();
}
hello();
Modules :
🔴 " Allow you to split code into separate files. "
🟩 Modules rely on import and export statements.
🟩 Send data using export and get data using import.
export const name = "Maharshi";
import {name,age} from "./file.js";
CallBacks() :
🔴 " function passed to another function as an argument. "
function print1(callback){
console.log("hello");
callback();
}
function print2(){
console.log("world");
}
print1(print2);
Promises :
🔴 " It is an object that links the producing code and consuming code. "
let myPromise = new
promise( function(myResolve, myReject){
// producing code
myResolve(); //Successful
myReject(); //error
});
// Consuming Code
myPromise.then(
function(value) { /* code if successful */},
function(error) { /* code if some error */}
);
Await :
🔴 " Awaits makes the function wait for a promise. "
let value = await promise;↪ await simply puts the statement on
waitStrict Mode :
🔴 " makes your js coding environment strict. "
🌟 Syntax :
"use strict";
🚀 Code will be executed in strict mode.
🚀 No undeclare variables can be used.
🚀 Makes you code more accurate.
Async :
🔴 " async is just a simple function returning a promise. "
async function mf(){ return "Hello"; }in same as :
function mf(){ return promise.resolve("Hello"); }JS Projects for Begineer :
💲 Js Stopwatch
💲 To-do List
💲 Weather app
💲 Tic Tac Toe app
💲 Music Player
So, That's all about JavaScript.
Reach me out in the comments below or in my socials : LinkdIn / Twitter to let me know what you think of it. Stay tuned for some more interesting blogs coming up soon.
Also, If you like my content and want to support my efforts please like👍🏻, share🔃 & subscribe to the newsletter 📩 to be get notified whenever I post a new blog.
Happy Coding !
Have a nice day :)

